The Great Pyramid:
It would be too great an omission for a site such as this to not have detail of the Great Pyramid of Giza, so here is a summary of some facts
Comprises 2.3 million blocks of stone
Each stone block weighs an average of 2.5 tons
Originally 481 feet high
Covers an area of 13 acres
The base is reportedly level to within 1.5 inches
The sides are orientated to the cardinal points of north, south, west and east to within an error of less that four feet.
The original entrance is 17 metres (56 ft) vertically above and 7.29 metres east of the center line of the pyramid.
The Tura limestone used for the casing was quarried across the river.
The largest granite stones in the pyramid, found in the “King’s” chamber, weigh 25 to 80 tons and were transported from Aswan, more than 800 km (500 mi) away.
The great pyramid was finished with blocks of white limestone, slant faced and highly polished, encasing it.
It’s latitude is 30 degrees north
The angle of slope is 51 degrees, (just over)
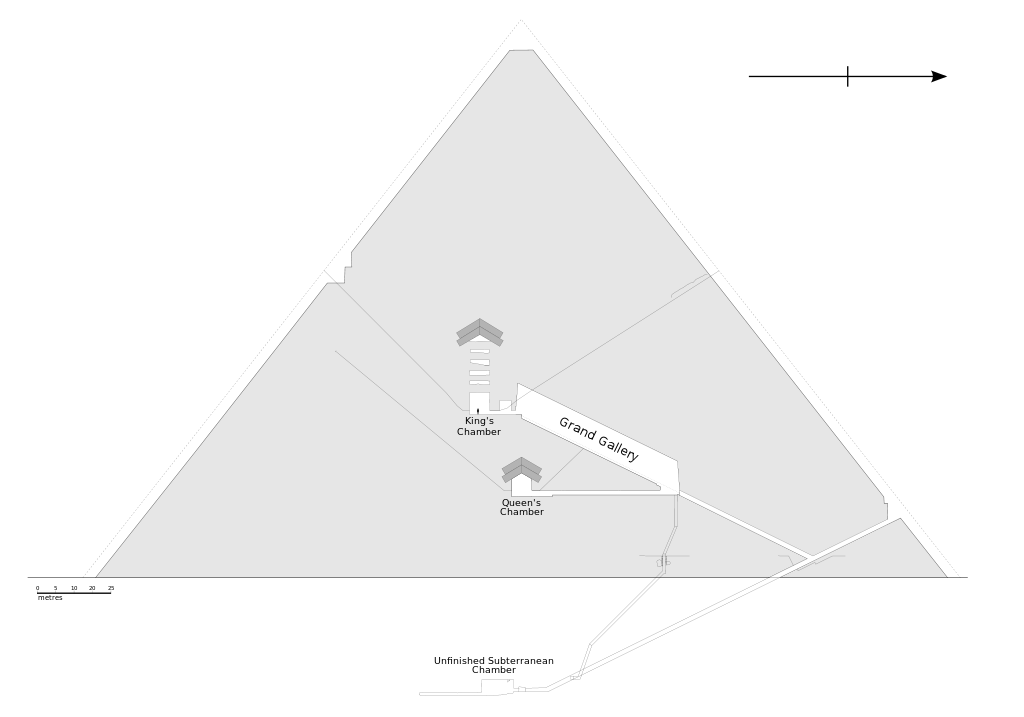
‘Queen’s’ Chamber:
It’s midway between north and south faces
Has a pointed roof with an apex
It has small shafts in the north and south walls which, after 2 metres, slope immediately but don’t reach the exterior of the pyramid.
The shafts are blocked by Limestone’ doors’ with two eroded copper ‘handles’
Behind the first ‘door’ in the southern shaft is another door
The rear of the first door is polished and the chamber between the doors has hieroglyphs in red paint.
At the eastern end of the chamber there is a niche 4.67 metres and originally 1.04 metres deep
At the end of one of his shafts, Dixon discovered a ball of black diorite and a bronze implement of unknown purpose. Both now in the British Museum.
‘King’s’ Chamber:
Has a flat roof
It has two narrow shafts, originally hidden, in the north and south walls which slope immediately but which do not reach the exterior of the pyramid
It’s entirely faced with granite
Nine granite slabs weighing a total of about 400 tons form the roof
Five compartments above the roof form Relieving Chambers, the v=base of each being flat with top one pointed.
A granite ‘sarcophagus is larger than the ascending access passage, hagus is slightly larger than the Ascending Passage, which indicates that it must have been placed in the Chamber before the roof was put in place.
Grand Gallery:
 An ascending passage is continued by a ‘grand gallery’ with corbelled walls in steve tiers, the top being 1.04 metres wide.
An ascending passage is continued by a ‘grand gallery’ with corbelled walls in steve tiers, the top being 1.04 metres wide.
Each of the gallery’s roof slabs fit into slots at the top, cut like the teeth of a ratchet.
The floor of the grand gallery is stepped, or shelved, to the sides with a central gutter same width as the Ascending Passage.
In the shelves are 54 slots, 27 on each side matched by vertical and horizontal slots in the walls of the Gallery (Speculation is wooden beams were inserted to restrain blocking stones from falling.
At the top of the Grand Gallery is a onto a horizontal passage approximately 1.02 metres in height and width.
In the passage is evidence of four slots, of which three, it is reportedly guessed as intended to hold granite portcullises.
Credits: Photo of Great Pyramid Nina-no, creative commons
Photo credit: Grand Gallery crosby_cj / Foter / CC BY-NC-ND
Credit: diagram By Jeff Dahl via Wikimedia Commons